Nepotism and favoritism have significant issues within Pakistan’s public sector, impacting everything from recruitment and promotions to the distribution of resources and the execution of policies. These practices undermine the principles of meritocracy. In Pakistan, the intertwining of political and bureaucratic spheres has often exacerbated these problems.
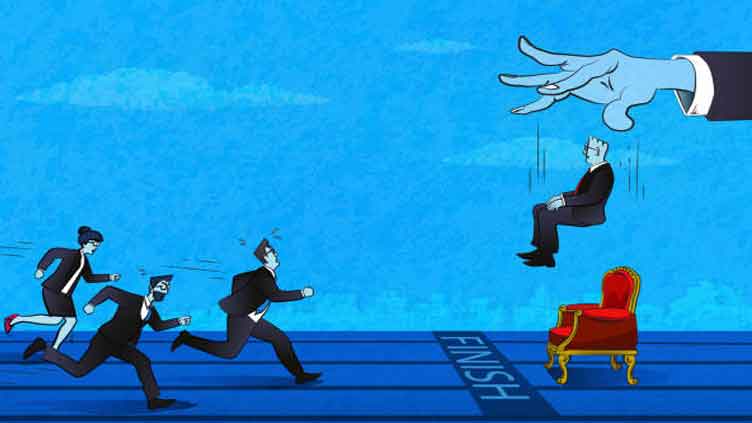
Political leaders frequently leverage their positions to secure advantageous roles for family members, friends, or loyalists. This form of nepotism not only affects the hiring processes but also influences promotions and departmental assignments. Such favoritism undermines the efficiency of public services, as positions may be filled based on personal connections rather than competence and qualifications.
- mostbet casino
- pin up casino
- mostbet казино
- 1win
- mostbet
- mostbet casino
- mosbet az
- mostbet kz казино
- mostbet casino
- lucky jet casino
- pinap
- mosbet
- mosbet az
- pinap
- pinup
- 1win casino
- mostbet kz
- 1win casino
- mosbet
- 1 win casino
- 1 win
- 1win casino bonus
- mostbet casino
- pin up uzbekistan
- 1win login
- mostbet
- 4era bet
- 1win casino
- snai casino it
- пин ап
- luckyjet
- pin up uzbekistan
- pin up casino
For instance, in various government departments, key positions have been occupied by individuals who are well-connected rather than well-qualified. This often results in poor decision-making and administrative inefficiencies, as the appointed individuals may lack the necessary expertise or commitment to their roles.
Nepotism and favoritism can perpetuate a cycle of corruption and inefficiency that affects the entire public sector as key roles are given to individuals based on connections rather than merit. Efforts to address these issues have been inconsistent.
While there are regulations and procedures in place intended to ensure fairness and transparency, their implementation is often weak. Anti-corruption bodies and oversight mechanisms may lack the authority or the will to enforce reforms effectively.
Ultimately, addressing nepotism and favoritism is essential not only for improving the functioning of the public sector but also for rebuilding trust between the government and its citizens. Only through sustained efforts and systemic change can Pakistan hope to overcome these entrenched challenges and move towards a more just and effective public administration.
Breaking the grip of nepotism and favoritism in Pakistan’s public sector is not merely a bureaucratic necessity it is a moral imperative tied to the nation’s democratic promise. These practices have not only compromised the effectiveness of governance but have also dimmed the hopes of a generation striving for fairness and opportunity.
True reform begins when merit is not the exception but the rule, and when public office is seen not as a privilege to be inherited, but a responsibility to be earned. Until then, Pakistan’s progress longer will remain hostage to connections rather than competence and the future will be written not by the most capable, but by the best connected
—-
Courtesy – Dunya News